Gums usually bleed because of the buildup of plaque at the gum line, which leads to a condition called gingivitis, or inflamed gums. If plaque is not removed at the right time, it will eventually harden into tartar. This will lead to increased bleeding and a more advanced form of gum and jawbone infection known as periodontitis. However, bleeding gums can also indicate various other health problems like diabetes, hormonal fluctuations, teeth grinding, and vitamin deficiencies.
If your gums bleed occasionally, you can heal yourself with good oral hygiene habits. But if gum bleeding becomes more frequent, you should seek help from a dental professional right away.
SYMPTOMS:
There are several symptoms of bleeding gums, including:
- Swollen or Puffy Gums
- Dusky Red or Dark Red Gums
- Bad Breath
- Receding Gums
- Tender Gums
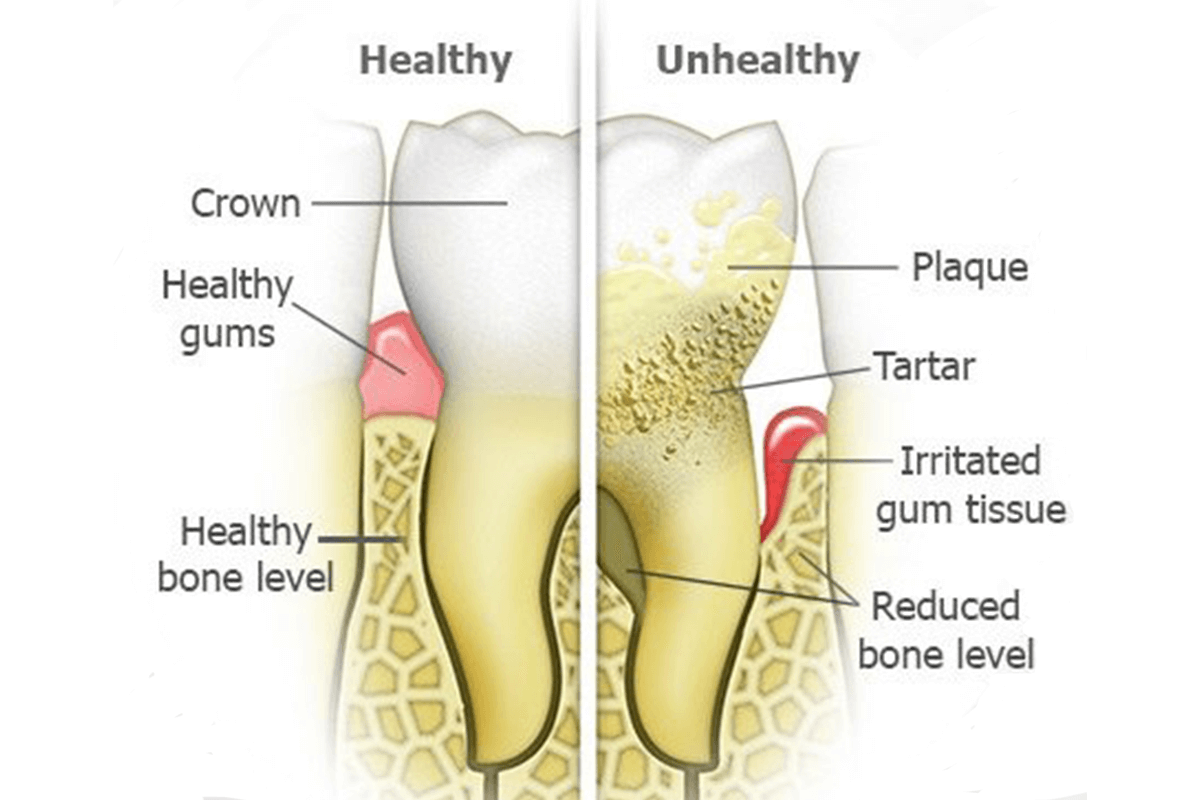
COMMON CAUSES OF BLEEDING GUMS:
There are various reasons that result in bleeding gums. However, the most common reason why gums bleed is poor oral hygiene routines that lead to the accumulation of plaque near the gum line. In addition to that, there are numerous other factors that contribute to gum bleeding and should be eliminated in order to prevent serious oral complications.
1. GINGIVITIS:
Gingivitis leads to plaque accumulation at the gum line, which is considered the primary cause of bleeding gums. If not removed, this condition eventually evolves into inflamed gums, where gums become dusky, swollen and frequently bleed while brushing. If not treated immediately, gingivitis can also lead to severe gum disease, which then contributes to tooth loss.
2. POOR DIET:
Gums can also bleed due to the consumption of a poor diet. Some processed foods contain certain ingredients that might irritate gums and cause minor bleeding. For example, food items rich in starch can get accumulated between the crevices of teeth and break down into sugar. It then results in plaque buildup. If you consume such foods regularly, they may lead to severe inflammation of the gums, bleeding, and increased decay.
In order to help prevent this, try to eat healthier food alternatives instead, as proper nutrition rich in vitamins and nutrients is essential for our oral health.
3. INTAKE OF CERTAIN MEDICATIONS:
Some medications can also become a contributing factor in increasing gum sensitivity and might lead to bleeding gums. For example, certain blood-thinning medications decrease our blood’s natural ability to clot and increase the chances of bleeding at the gum line. Other medications such as birth control, aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs, and some blood pressure medications can also enhance your risk of developing gum-related issues.
Therefore, make sure to inform your dental professional about all the medications that you are taking, particularly if your gums bleed on a regular basis. This might help dentists determine oral health problems in a more precise way. In such cases, dentists might also recommend a different oral care program in order to minimize or prevent bleeding caused by medications.
4. BRUSHING TOO HARD:
Harshly brushing your teeth does not clean your teeth in a better way; instead, it puts an extra strain on your teeth and increases your risk of developing gum recession. Therefore, if you are facing a gum-related issue, adjust your brushing technique and opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush.
5. HEALTH PROBLEMS:
Certain health conditions might also lead to gum bleeding. It is usually more common in patients with certain health problems, like liver disease, Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, vitamin K deficiency, blood clotting disorders, anemia, leukemia, and temporal arteritis.
6. MISALIGNED BITE:
Another issue that contributes to bleeding gums is a misaligned bite. You are relatively at higher risk of developing gum issues if your teeth are not properly positioned. A misaligned bite exerts pressure on the wrong places when you chew food or grind your teeth. If repeated pressure is continuously applied in one spot, the gums might eventually recede, deteriorating the bone underneath and creating a prime spot for bleeding.
TREATMENTS FOR BLEEDING GUMS:
You can treat tender and bleeding gums by performing proper oral hygiene routines. But in case your gum recession has reached more advanced stages, it can no longer be treated at home, and you might require professional dental treatments.
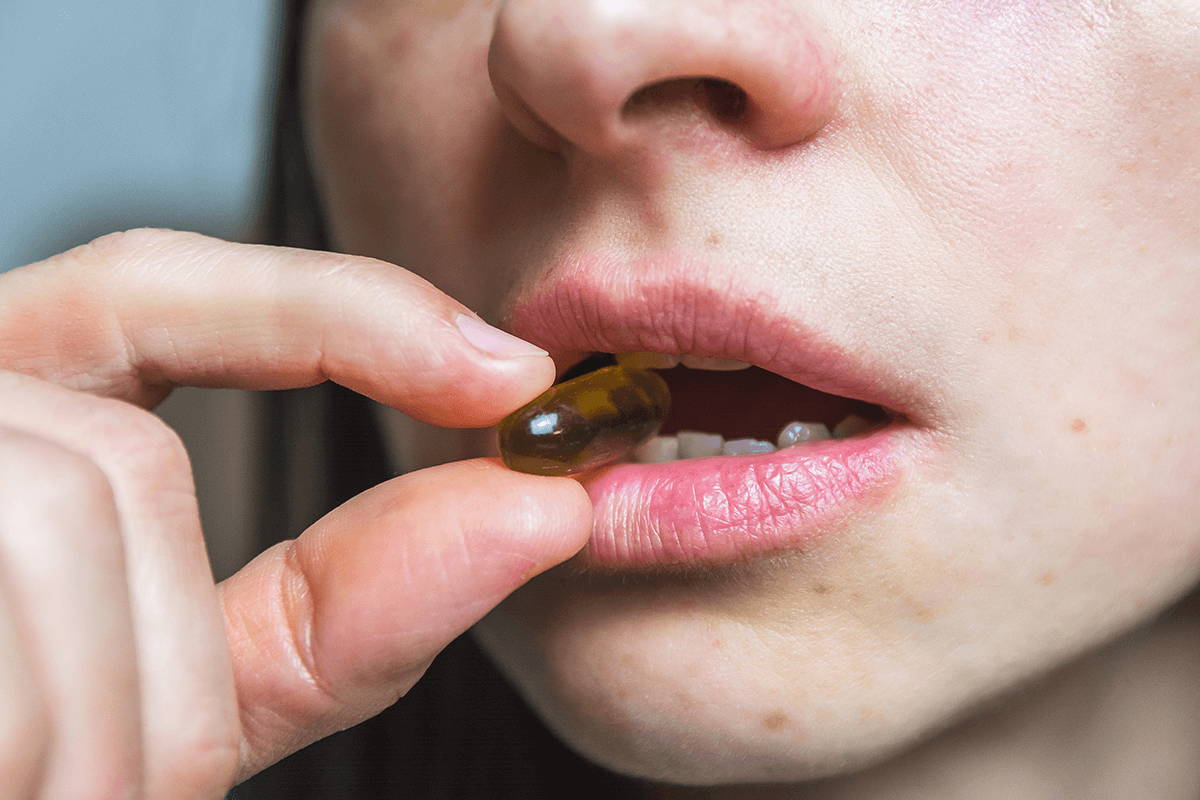
1. ANTIBIOTICS:
The intake of certain antibiotics can treat various gum issues and help prevent bleeding gums. Oral antibiotics for dental infection usually include tetracycline, hydrochloride and minocycline. These medicines treat inflammation by obstructing a protein called collagenase, which can destroy connective tissues in our mouth.

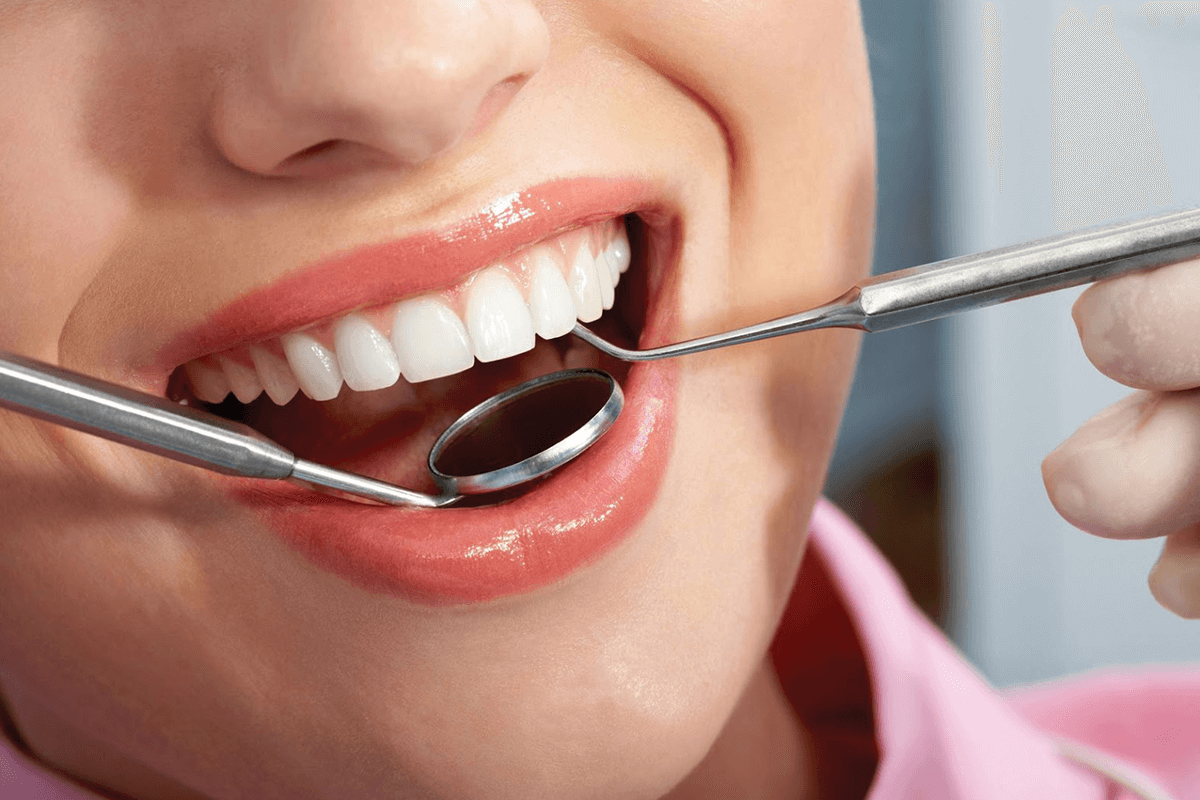
2. TOOTH SCALING:
This treatment generally includes a series of root planning and deep cleanings. During these processes, bacteria accumulated between the gum pockets of your teeth are thoroughly removed.
This process helps dentists effectively eliminate deep-rooted plaque present between the crevices of your teeth. As a result, this also helps improve your overall oral health. This type of dental treatment is usually recommended for patients who are suffering from chronic periodontitis. However, in general, it also proves to be beneficial for anyone experiencing bleeding gums for an extended period.
3. OSSEOUS SURGERY:
Osseous surgery is another option that can help treat mouths plagued with periodontal diseases. It effectively eliminates tartar sticking to the root surfaces of your teeth. In this way, it provides a healthy attachment of the gums to teeth and eventually eliminates gum bleeding problems.
It is a type of dental procedure used to treat moderate to severe periodontal problems. The primary goal of this surgery is to reduce the pockets around your teeth, so plaque cannot accumulate there.
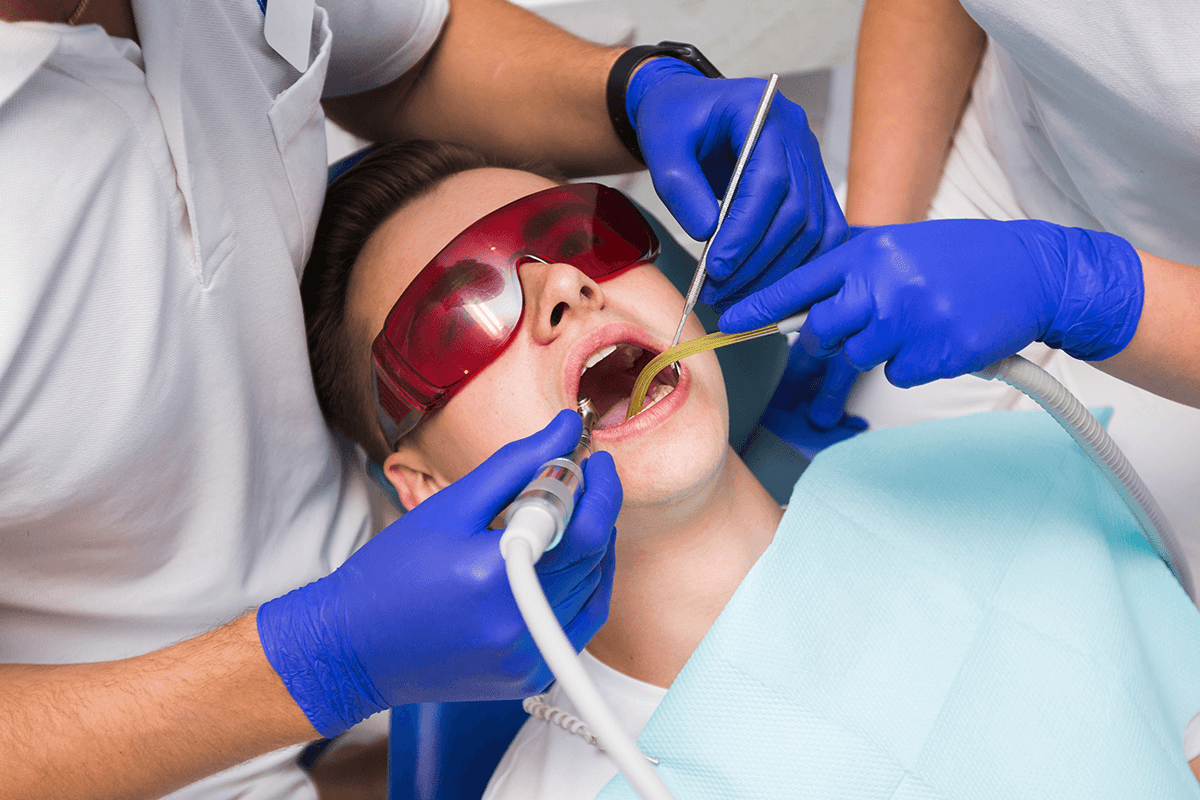
4. LASER PERIODONTAL SURGERY:
Periodontal laser therapy is a very effective treatment option for bleeding gums. In this therapy, periodontists typically use a laser to access and remove the inflamed gum tissue from the patient’s tooth’s root. They then remove the tartar below and around the gum line. Next, they use a tool to smooth out rough spots on the surface of the patient’s tooth above and below the gum line.
The laser used in this procedure can also cauterize the tissue. This significantly helps reduce bleeding and post-surgical discomfort. Dental professionals sometimes also use the laser used in this procedure to correct and reshape the underlying jawbone.










